

Adding content to your website is important for you and your business, but ensuring that it looks professional and helps Google and other search engines find and rank your webpage is crucial. Headings play an important role here.
While you might think that headings in content are only for the design of your webpage, they are a critical SEO element that we need to get right. Headings serve as signals to search engines and your users as to what’s important on your page, and what the page is about. In this post, we explore how to use headings on website pages to ensure your page can be read by humans and indexed by search engines.
Let’s go into more detail.
When you’re setting content up on your website, nearly every platform will have a dropdown menu where you can pick your heading. It should look something like this:
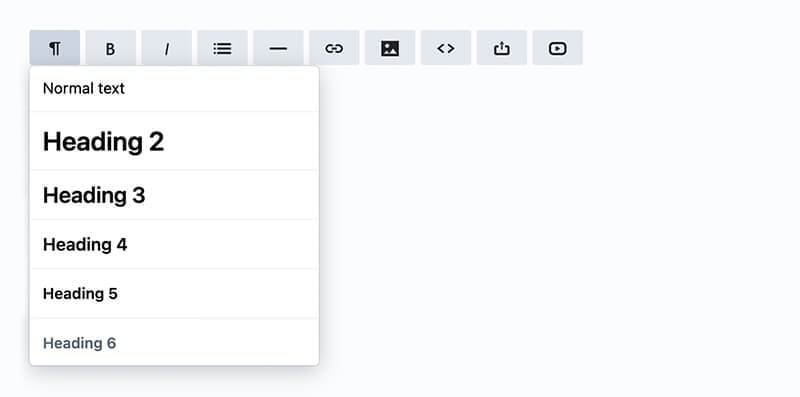
Choosing a heading from this dropdown alters your content code, styling your text as a heading, and tagging it for search engines. There are six levels of headings available.
Headings are generally part of your website’s overall design, and your web designer will have usually styled these to be attention-grabbing, easy to recognise and with high readability. By selecting a certain heading preset within your content management system, you’re staying on-brand with your design and this helps keep your website accessible and readable by your users. This is a better approach than using bold or manually changing text sizes.
The H1 heading is reserved for the name of your webpage or the name of your article and this is the only place you should use the H1 heading.
The Heading One signals to search engines what your page is about. It’s like naming a book. Books have one title and it’s in a big font on the front cover. When you see it, you know what it’s called and probably what it’s about.
Your website will often be set up in a way that will use the page title as your heading one, so you won’t manually need to define a heading one on your page.
The important thing with H1 headings is to not use them again on your page. After you put the title in, leave the rest as H2 headings or other heading numbers.
Resource: How to create the perfect H1 tag for SEO (Neil Patel)
Most of the headings you will use on your webpage will likely be H2. Google pays attention to H2 headings and the words that are in those headings to figure out what your article is about and how to rank it in search results. If you’re unsure, make your heading a heading two.
H2 headings are great at breaking up long-form content. It provides context to your users and search engines about the following paragraphs they’re about to read and helps them scan the page to find the information they’re looking for.
In a standard web page, breaking up your content every couple of hundred words or less with a new heading two ensures that your content is easy-to-read. You can further break down these sections with headings three through five or six, depending on your website editor.
It’s important to remember that a heading with a lower number needs to precede any heading, which is important for your lower headings. There is some room to play with styles here, as you don’t have to use the Heading Three (H3) if you need your title styled smaller like the Heading Four (H4). Just be sure you’ve got the H2 heading above it. It's important to note that using these levels of headings isn't required if your content doesn't call for it.
Google doesn’t put as much weight into the keywords you use for these headings as it does for H2 headings but it all helps Google to understand what your page is about.
Learn more on this and other bits of code or Semantic HTML you can use on your website.
One important concept to understand when it comes to headings is to structure them in a hierarchy. The easiest way to understand this is in a business structure:
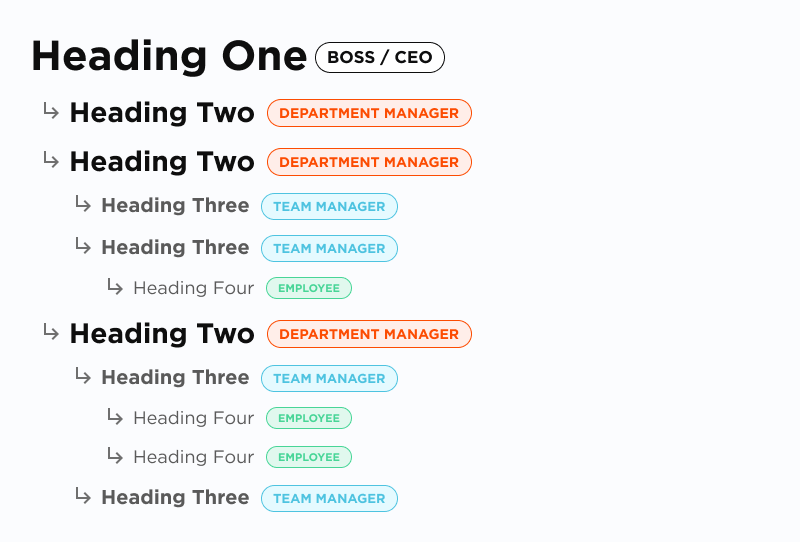
So we have one boss - H1, multiple managers - H2, and employees under those managers - H3-H6.
One of the easier SEO tactics you can use is to put your important keywords (words people search for) in your headings, especially your H2 headings.
Your H1 heading should contain the main keyword for the page which tells Google what your page is about.
For your H2 headings, you can also use your main keyword at least once, and if there’s a way to say your keyword differently and include it in your heading, that’s also a great idea. This helps capture more potential searches by users.
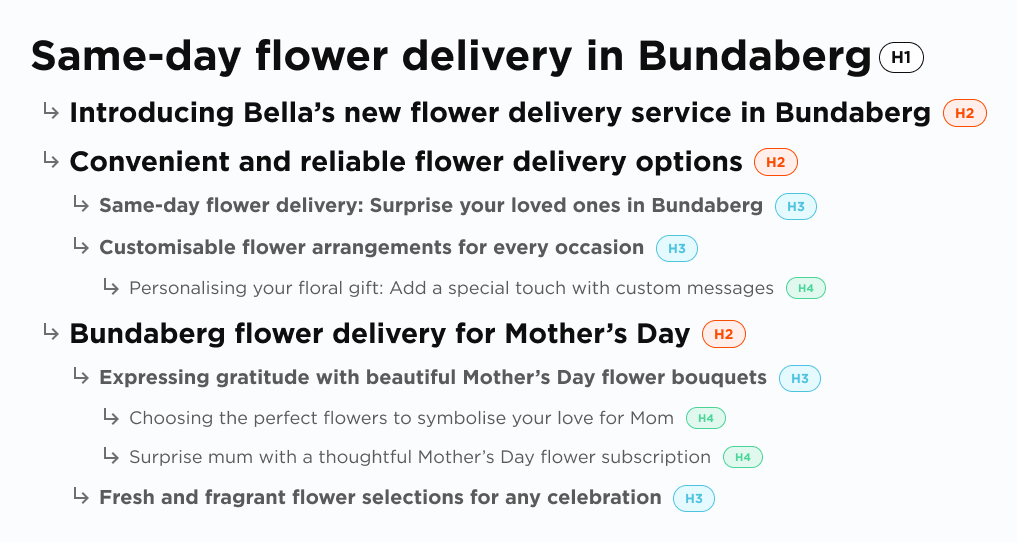
For a key service page on the website of a theoretical company, "Bella's Flowers", we can see how this can potentially be laid out to break up the content into readable sections.
Main keyword: flower delivery in Bundaberg
Page title (H1): Same-day flower delivery in Bundaberg
Similar keywords:
H2 heading: Introducing Bella’s new flower delivery service in Bundaberg
H2 heading: Convenient and reliable flower delivery options
H2 heading: Bundaberg flower delivery for Mother's Day
Using keywords in other headings (H3-H6) is still a good idea and helps Google to understand what your page is about and makes it easier to read.
If we were to create a page outline using different types of headings for Bella’s Flowers, here’s what it could look like:
When it comes to headings and page structure, a website built by web designers and web developers will usually have been created to ensure your headings are easy to use, styled for optimal reading by your users, and set up correctly to be understood by Google. Your job is to use these headings within your content.
The great news is that following these simple steps will keep your website looking great and give users a higher chance of finding your information and business online.
Header tags: what they are and how to use them (Hubspot)
How to write catchy headlines (Hubspot)
Semantic HTML: What It Is and How to Use It Correctly (SemRush)
Google explains how to use headings for SEO (Search Engine Journal)
© 2025 Itag Media | Legals | Privacy Policy | Site Map
your brand. made better